Sleeplessness or Insomnia
Insomnia is a sleep disorder where people have trouble falling or staying asleep. Sometimes people refer to it as “sleeplessness”. Understandably, insomnia is often associated with daytime drowsiness, tiredness, irritability, and depression. Insomnia can be short-term or can last weeks, months, or years without treatment.
Signs and symptoms of insomnia include:
- difficulty falling asleep
- waking during the night and being unable to return to sleep
- feeling unrefreshed upon waking
- daytime sleepiness, irritability, or anxiety
Our psychologists and psychotherapists can help. We are trained in cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) techniques for treatment of insomnia.
What Causes Insomnia?
- Starting or stopping certain medications
- Use of stimulants, caffeine or nicotine, or excessive alcohol use
- Chronic pain that interferes with sleep
- Shifting hormone levels
- Stressful life events
- Mental conditions like depression, anxiety disorders, post traumatic stress disorder, or ADHD
- Shift work and jet lag
- Traumatic brain injury
- Poor sleep hygiene (excessive “screen time” before bed, consuming caffeine before bed, staying up too late)
- Increased exposure to the blue light from artificial sources, such as phones or computers
Treatments for Insomnia
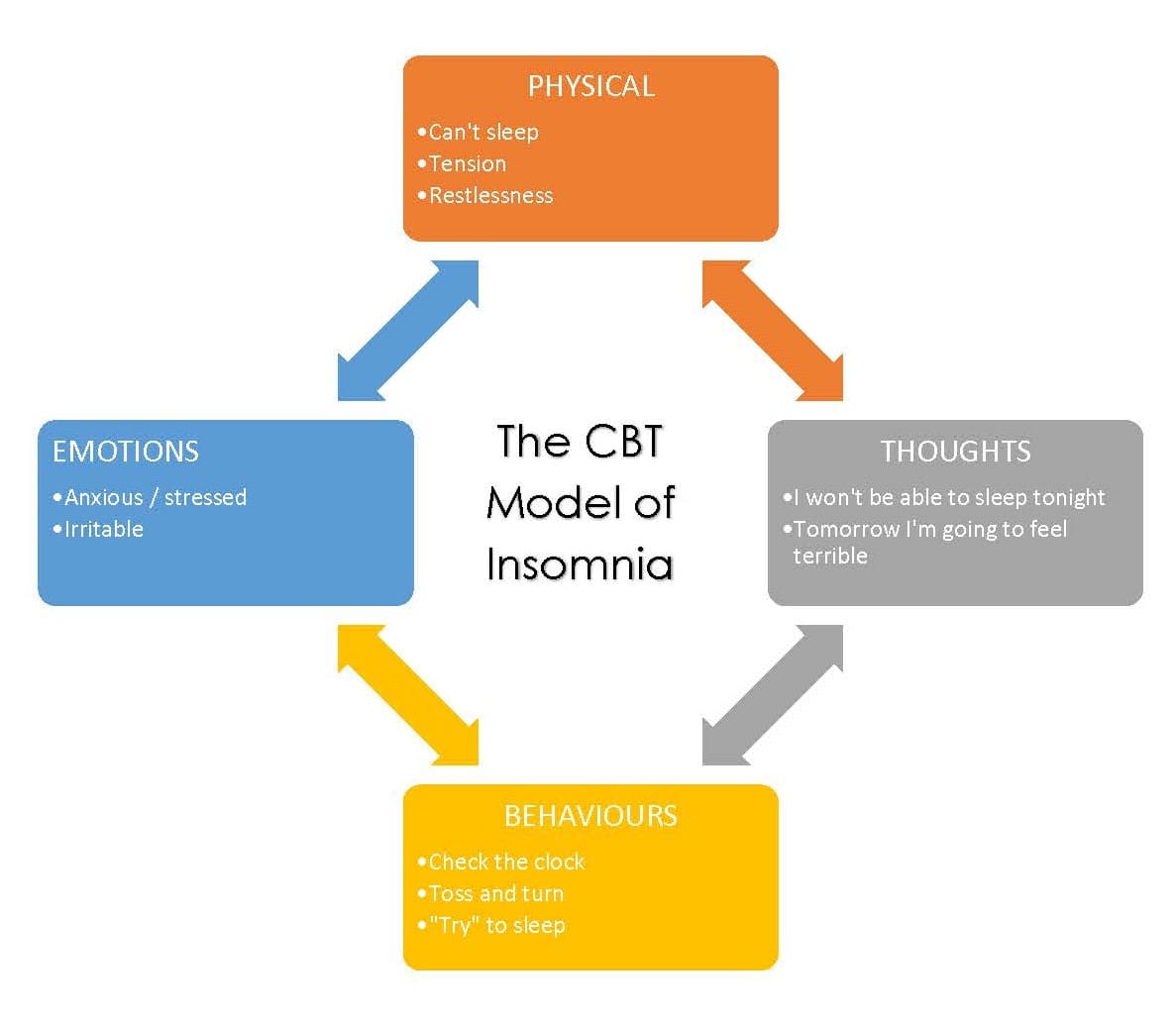
Insomnia can be treated using cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), medications (like Imovane or melatonin) and “sleep hygiene” strategies.
Cognitive behaviour therapy helps people to overcome the negative cycle of insomnia.
Sleep Hygiene
 Sleep hygiene refers to practices and habits that we do every day to promote good sleep:
Sleep hygiene refers to practices and habits that we do every day to promote good sleep:
- Avoid or limit daytime naps – If you must nap, keep it shorter than 30 minutes!
- Avoid stimulants like caffeine and nicotine close to bedtime.
- Avoid alcohol before bed – While alcohol can make you feel sleepy, too much alcohol close to bedtime makes you more prone to waking through the night.
- Exercise during the day but not too close to bedtime.
- Try to avoid eating heavy meals or rich, spicy, or fatty foods before bed – this can trigger indigestion or heartburn that will keep you awake.
- Make sure you are exposed to natural light during the day and darkness at night – this tells our body when it is time to sleep.
- Create and stick to a relaxing bedtime routine – Around the same time each night, try taking a warm bath, drinking caffeine free tea, or meditating before bed.
- Create a sleep-promoting bedroom – Most people sleep best when the room temperature is between 60 to 67 degrees. Try using blackout curtains, ear plugs, a “white noise” machine, humidifier, or fan to block light and noises that might disturb your sleep.